Gemini API, फ़ाइल खोजने वाले टूल की मदद से, रीट्रिवल ऑगमेंटेड जनरेशन ("आरएजी") की सुविधा देता है. फ़ाइल खोज की सुविधा, आपके डेटा को इंपोर्ट करती है, उसे छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों में बांटती है, और इंडेक्स करती है. इससे दिए गए प्रॉम्प्ट के आधार पर, काम की जानकारी को तेज़ी से वापस पाने में मदद मिलती है. इसके बाद, इस जानकारी का इस्तेमाल मॉडल के लिए कॉन्टेक्स्ट के तौर पर किया जाता है. इससे मॉडल को ज़्यादा सटीक और काम के जवाब देने में मदद मिलती है.
हम फ़ाइल स्टोरेज और क्वेरी के समय एम्बेड जनरेट करने की सुविधा को बिना किसी शुल्क के उपलब्ध करा रहे हैं. इससे डेवलपर के लिए, फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा को इस्तेमाल करना आसान और किफ़ायती हो जाएगा. आपको सिर्फ़ एम्बेडिंग बनाने के लिए शुल्क देना होता है. यह शुल्क तब लिया जाता है, जब पहली बार अपनी फ़ाइलों को इंडेक्स किया जाता है. यह शुल्क, एम्बेडिंग मॉडल पर लागू होने वाली लागत के हिसाब से लिया जाता है. इसके अलावा, Gemini मॉडल के इनपुट / आउटपुट टोकन की सामान्य लागत भी ली जाती है. बिलिंग के इस नए मॉडल की वजह से, फ़ाइल खोजने वाले टूल को बनाना और उसे स्केल करना, दोनों ही आसान और किफ़ायती हो गया है.
फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर में सीधे अपलोड करें
इस उदाहरण में, फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर में फ़ाइल को सीधे अपलोड करने का तरीका बताया गया है:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file='sample.txt',
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
config={
'display_name' : 'display-file-name',
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, uploadToFileSearchStore का एपीआई रेफ़रंस देखें.
फ़ाइलें इंपोर्ट करना
इसके अलावा, आपके पास किसी मौजूदा फ़ाइल को अपलोड करने और उसे फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा के लिए बनाए गए स्टोर में इंपोर्ट करने का विकल्प भी है:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
sample_file = client.files.upload(file='sample.txt', config={'name': 'display_file_name'})
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const sampleFile = await ai.files.upload({
file: 'sample.txt',
config: { name: 'file-name' }
});
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation: operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, importFile का एपीआई रेफ़रंस देखें.
डेटा को छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों में बांटने का कॉन्फ़िगरेशन
किसी फ़ाइल को File Search स्टोर में इंपोर्ट करने पर, वह अपने-आप छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों में बंट जाती है. साथ ही, उसे एंबेड किया जाता है, इंडेक्स किया जाता है, और आपके File Search स्टोर में अपलोड किया जाता है. अगर आपको चंकिंग की रणनीति पर ज़्यादा कंट्रोल चाहिए, तो chunking_config सेटिंग का इस्तेमाल करें. इससे, हर चंक के लिए ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा टोकन और ओवरलैप होने वाले टोकन की ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा संख्या सेट की जा सकती है.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
config={
'chunking_config': {
'white_space_config': {
'max_tokens_per_chunk': 200,
'max_overlap_tokens': 20
}
}
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
print("Custom chunking complete.")
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
chunkingConfig: {
whiteSpaceConfig: {
maxTokensPerChunk: 200,
maxOverlapTokens: 20
}
}
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
console.log("Custom chunking complete.");
फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाले स्टोर का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, इसे generateContent
मेथड में टूल के तौर पर पास करें. इसके लिए, अपलोड करें और इंपोर्ट करें के उदाहरण देखें.
यह कैसे काम करता है
फ़ाइल खोज, सिमैंटिक सर्च नाम की तकनीक का इस्तेमाल करके, उपयोगकर्ता के प्रॉम्प्ट से जुड़ी जानकारी ढूंढती है. कीवर्ड के आधार पर की जाने वाली स्टैंडर्ड सर्च के उलट, सिमैंटिक सर्च आपकी क्वेरी के मतलब और कॉन्टेक्स्ट को समझती है.
किसी फ़ाइल को इंपोर्ट करने पर, उसे संख्या के तौर पर दिखाया जाता है. इसे एम्बेडिंग कहा जाता है. इससे टेक्स्ट के सिमैंटिक मतलब का पता चलता है. इन एम्बेडिंग को, फ़ाइल खोज के खास डेटाबेस में सेव किया जाता है. क्वेरी करने पर, उसे भी एम्बेडिंग में बदल दिया जाता है. इसके बाद, सिस्टम फ़ाइल खोज की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करके, फ़ाइल खोज के स्टोर से मिलते-जुलते और काम के दस्तावेज़ के हिस्सों को ढूंढता है.
एम्बेड किए गए कॉन्टेंट और फ़ाइलों के लिए, टाइम टू लिव (टीटीएल) की सुविधा उपलब्ध नहीं है. ये तब तक सेव रहती हैं, जब तक इन्हें मैन्युअल तरीके से नहीं मिटाया जाता या मॉडल को बंद नहीं कर दिया जाता.
फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाले uploadToFileSearchStore एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करने की प्रोसेस के बारे में यहां बताया गया है:
फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर बनाएं: फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर में, आपकी फ़ाइलों से प्रोसेस किया गया डेटा होता है. यह एम्बेडिंग के लिए परसिस्टेंट कंटेनर है. इस पर सिमैंटिक सर्च काम करेगी.
कोई फ़ाइल अपलोड करना और उसे फ़ाइल खोजने वाले स्टोर में इंपोर्ट करना: एक साथ कोई फ़ाइल अपलोड करें और नतीजों को फ़ाइल खोजने वाले स्टोर में इंपोर्ट करें. इससे एक अस्थायी
Fileऑब्जेक्ट बनता है, जो आपके रॉ दस्तावेज़ का रेफ़रंस होता है. इसके बाद, उस डेटा को छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों में बांटा जाता है. साथ ही, उसे फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा के लिए एम्बेड किए गए डेटा में बदलकर इंडेक्स किया जाता है.Fileऑब्जेक्ट 48 घंटे बाद मिट जाता है. वहीं, फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाले स्टोर में इंपोर्ट किया गया डेटा, हमेशा के लिए सेव रहता है. हालांकि, इसे तब तक सेव रखा जाता है, जब तक इसे मिटाने का विकल्प नहीं चुना जाता.फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा के साथ क्वेरी: आखिर में,
generateContentकॉल मेंFileSearchटूल का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. टूल कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में, आपको एकFileSearchRetrievalResourceतय करना होता है. यहFileSearchStoreकी ओर इशारा करता है, जिसे आपको खोजना है. इससे मॉडल को उस फ़ाइल सर्च स्टोर पर सिमैंटिक सर्च करने का निर्देश मिलता है, ताकि वह अपने जवाब के लिए काम की जानकारी ढूंढ सके.
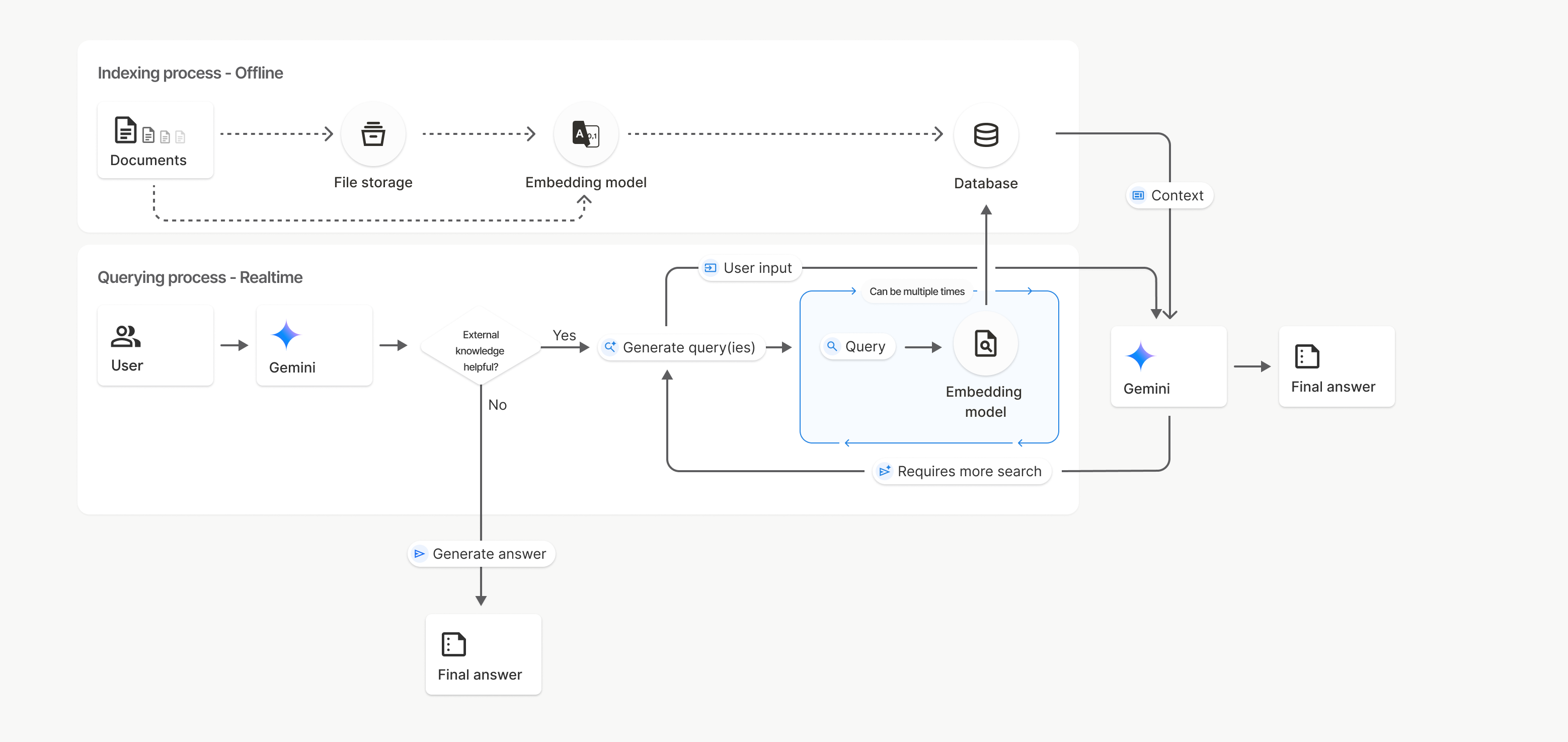
इस डायग्राम में, दस्तावेज़ से एम्बेडिंग मॉडल तक की डॉटेड लाइन (gemini-embedding-001 का इस्तेमाल करके) uploadToFileSearchStore एपीआई को दिखाती है. इसमें फ़ाइल स्टोरेज को बायपास किया जाता है.
इसके अलावा, Files API का इस्तेमाल करके, फ़ाइलों को अलग से बनाने और फिर इंपोर्ट करने से, इंडेक्स करने की प्रोसेस Documents से File storage और फिर Embedding model पर चली जाती है.
फ़ाइल खोजें
फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाला स्टोर, आपके दस्तावेज़ों के एम्बेड किए गए वर्शन के लिए कंटेनर होता है. File API के ज़रिए अपलोड की गई रॉ फ़ाइलें, 48 घंटे बाद मिट जाती हैं. हालांकि, फ़ाइल सर्च स्टोर में इंपोर्ट किया गया डेटा तब तक सेव रहता है, जब तक उसे मैन्युअल तरीके से नहीं मिटाया जाता. अपने दस्तावेज़ों को व्यवस्थित करने के लिए, एक से ज़्यादा फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर बनाए जा सकते हैं. FileSearchStore API की मदद से, फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर को मैनेज करने के लिए, फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर बनाए जा सकते हैं, उनकी सूची बनाई जा सकती है, उन्हें पाया जा सकता है, और उन्हें मिटाया जा सकता है. फ़ाइल खोज में स्टोर के नाम, दुनिया भर में उपलब्ध होते हैं.
यहां कुछ उदाहरण दिए गए हैं, जिनसे आपको फ़ाइल खोज की सुविधा वाले स्टोर मैनेज करने के तरीके के बारे में जानकारी मिलेगी:
Python
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'my-file_search-store-123'})
for file_search_store in client.file_search_stores.list():
print(file_search_store)
my_file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123')
client.file_search_stores.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123', config={'force': True})
JavaScript
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'my-file_search-store-123' }
});
const fileSearchStores = await ai.fileSearchStores.list();
for await (const store of fileSearchStores) {
console.log(store);
}
const myFileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123',
config: { force: true }
});
REST
curl -X POST "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{ "displayName": "My Store" }'
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
फ़ाइल खोजने से जुड़े दस्तावेज़
File Search Documents API की मदद से, फ़ाइल स्टोर में मौजूद अलग-अलग दस्तावेज़ों को मैनेज किया जा सकता है. इससे, फ़ाइल सर्च स्टोर में मौजूद list हर दस्तावेज़, get किसी दस्तावेज़ के बारे में जानकारी, और नाम के हिसाब से delete कोई दस्तावेज़ खोजा जा सकता है.
Python
for document_in_store in client.file_search_stores.documents.list(parent='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'):
print(document_in_store)
file_search_document = client.file_search_stores.documents.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
print(file_search_document)
client.file_search_stores.documents.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
JavaScript
const documents = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.list({
parent: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
for await (const doc of documents) {
console.log(doc);
}
const fileSearchDocument = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
फ़ाइल का मेटाडेटा
फ़ाइलों को फ़िल्टर करने या उनके बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी देने के लिए, उनमें कस्टम मेटाडेटा जोड़ा जा सकता है. मेटाडेटा, की-वैल्यू पेयर का एक सेट होता है.
Python
op = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
custom_metadata=[
{"key": "author", "string_value": "Robert Graves"},
{"key": "year", "numeric_value": 1934}
]
)
JavaScript
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name,
config: {
customMetadata: [
{ key: "author", stringValue: "Robert Graves" },
{ key: "year", numericValue: 1934 }
]
}
});
यह तब काम आता है, जब आपके पास फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाले स्टोर में कई दस्तावेज़ हों और आपको सिर्फ़ उनमें से कुछ दस्तावेज़ों को खोजना हो.
Python
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name],
metadata_filter="author=Robert Graves",
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name],
metadataFilter: 'author="Robert Graves"',
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[{"text": "Tell me about the book I, Claudius"}]
}],
"tools": [{
"file_search": {
"file_search_store_names":["'$STORE_NAME'"],
"metadata_filter": "author = \"Robert Graves\""
}
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
metadata_filter के लिए, सूची वाले फ़िल्टर के सिंटैक्स को लागू करने के बारे में दिशा-निर्देश यहां दिए गए हैं: google.aip.dev/160
उद्धरण
फ़ाइल खोज सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करने पर, मॉडल के जवाब में उद्धरण शामिल हो सकते हैं. इनमें यह जानकारी होती है कि जवाब जनरेट करने के लिए, अपलोड किए गए दस्तावेज़ों के किन हिस्सों का इस्तेमाल किया गया है. इससे तथ्यों की जांच और पुष्टि करने में मदद मिलती है.
जवाब के grounding_metadata एट्रिब्यूट के ज़रिए, उद्धरण की जानकारी ऐक्सेस की जा सकती है.
Python
print(response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata)
JavaScript
console.log(JSON.stringify(response.candidates?.[0]?.groundingMetadata, null, 2));
स्ट्रक्चर्ड आउटपुट
Gemini 3 मॉडल से शुरू करके, फ़ाइल खोजने वाले टूल को स्ट्रक्चर्ड आउटपुट के साथ इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
Python
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Money(BaseModel):
amount: str = Field(description="The numerical part of the amount.")
currency: str = Field(description="The currency of amount.")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
],
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=Money.model_json_schema()
)
)
result = Money.model_validate_json(response.text)
print(result)
JavaScript
import { z } from "zod";
const moneySchema = z.object({
amount: z.string().describe("The numerical part of the amount."),
currency: z.string().describe("The currency of amount."),
});
async function run() {
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [file_search_store.name],
},
},
],
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseJsonSchema: z.toJSONSchema(moneySchema),
},
});
const result = moneySchema.parse(JSON.parse(response.text));
console.log(result);
}
run();
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts": [{"text": "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?"}]
}],
"tools": [
{
"fileSearch": {
"fileSearchStoreNames": ["$FILE_SEARCH_STORE_NAME"]
}
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"responseMimeType": "application/json",
"responseJsonSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"amount": {"type": "string", "description": "The numerical part of the amount."},
"currency": {"type": "string", "description": "The currency of amount."}
},
"required": ["amount", "currency"]
}
}
}'
काम करने वाले मॉडल
फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा, इन मॉडल के साथ काम करती है:
इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले फ़ाइल टाइप
फ़ाइल ढूंढने की सुविधा, कई तरह के फ़ाइल फ़ॉर्मैट के साथ काम करती है. इनकी जानकारी यहां दी गई है.
ऐप्लिकेशन फ़ाइल के टाइप
application/dartapplication/ecmascriptapplication/jsonapplication/ms-javaapplication/mswordapplication/pdfapplication/sqlapplication/typescriptapplication/vnd.curlapplication/vnd.dartapplication/vnd.ibm.secure-containerapplication/vnd.jupyterapplication/vnd.ms-excelapplication/vnd.oasis.opendocument.textapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentationapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheetapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.documentapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.templateapplication/x-cshapplication/x-hwpapplication/x-hwp-v5application/x-latexapplication/x-phpapplication/x-powershellapplication/x-shapplication/x-shellscriptapplication/x-texapplication/x-zshapplication/xmlapplication/zip
टेक्स्ट फ़ाइल के टाइप
text/1d-interleaved-parityfectext/REDtext/SGMLtext/cache-manifesttext/calendartext/cqltext/cql-extensiontext/cql-identifiertext/csstext/csvtext/csv-schematext/dnstext/encaprtptext/enrichedtext/exampletext/fhirpathtext/flexfectext/fwdredtext/gff3text/grammar-ref-listtext/hl7v2text/htmltext/javascripttext/jcr-cndtext/jsxtext/markdowntext/mizartext/n3text/parameterstext/parityfectext/phptext/plaintext/provenance-notationtext/prs.fallenstein.rsttext/prs.lines.tagtext/prs.prop.logictext/raptorfectext/rfc822-headerstext/rtftext/rtp-enc-aescm128text/rtploopbacktext/rtxtext/sgmltext/shaclctext/shextext/spdxtext/stringstext/t140text/tab-separated-valuestext/texmacstext/trofftext/tsvtext/tsxtext/turtletext/ulpfectext/uri-listtext/vcardtext/vnd.DMClientScripttext/vnd.IPTC.NITFtext/vnd.IPTC.NewsMLtext/vnd.atext/vnd.abctext/vnd.ascii-arttext/vnd.curltext/vnd.debian.copyrighttext/vnd.dvb.subtitletext/vnd.esmertec.theme-descriptortext/vnd.exchangeabletext/vnd.familysearch.gedcomtext/vnd.ficlab.flttext/vnd.flytext/vnd.fmi.flexstortext/vnd.gmltext/vnd.graphviztext/vnd.hanstext/vnd.hgltext/vnd.in3d.3dmltext/vnd.in3d.spottext/vnd.latex-ztext/vnd.motorola.reflextext/vnd.ms-mediapackagetext/vnd.net2phone.commcenter.commandtext/vnd.radisys.msml-basic-layouttext/vnd.senx.warpscripttext/vnd.sositext/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptortext/vnd.trolltech.linguisttext/vnd.wap.sitext/vnd.wap.sltext/vnd.wap.wmltext/vnd.wap.wmlscripttext/vtttext/wgsltext/x-asmtext/x-bibtextext/x-bootext/x-ctext/x-c++hdrtext/x-c++srctext/x-cassandratext/x-chdrtext/x-coffeescripttext/x-componenttext/x-cshtext/x-csharptext/x-csrctext/x-cudatext/x-dtext/x-difftext/x-dsrctext/x-emacs-lisptext/x-erlangtext/x-gff3text/x-gotext/x-haskelltext/x-javatext/x-java-propertiestext/x-java-sourcetext/x-kotlintext/x-lilypondtext/x-lisptext/x-literate-haskelltext/x-luatext/x-moctext/x-objcsrctext/x-pascaltext/x-pcs-gcdtext/x-perltext/x-perl-scripttext/x-pythontext/x-python-scripttext/x-r-markdowntext/x-rsrctext/x-rsttext/x-ruby-scripttext/x-rusttext/x-sasstext/x-scalatext/x-schemetext/x-script.pythontext/x-scsstext/x-setexttext/x-sfvtext/x-shtext/x-siestatext/x-sostext/x-sqltext/x-swifttext/x-tcltext/x-textext/x-vbasictext/x-vcalendartext/xmltext/xml-dtdtext/xml-external-parsed-entitytext/yaml
सीमाएं
- Live API: फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा, Live API में काम नहीं करती.
- टूल के साथ काम न करना: फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा को फ़िलहाल, Google Search से मिली जानकारी का इस्तेमाल करके जवाब देने की सुविधा, यूआरएल के कॉन्टेक्स्ट वगैरह जैसे अन्य टूल के साथ इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता.
तय सीमाएं
सेवा को बेहतर तरीके से चलाने के लिए, File Search API पर ये सीमाएं लागू होती हैं:
- फ़ाइल का ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा साइज़ / हर दस्तावेज़ के लिए सीमा: 100 एमबी
- प्रोजेक्ट फ़ाइल खोज के लिए उपलब्ध स्टोरेज का कुल साइज़ (उपयोगकर्ता के टियर के आधार पर):
- मुफ़्त: 1 जीबी
- टियर 1: 10 जीबी
- टियर 2: 100 जीबी
- टियर 3: 1 टीबी
- सुझाव: हर फ़ाइल खोज स्टोर का साइज़ 20 जीबी से कम रखें, ताकि फ़ाइलें खोजने में कम समय लगे.
कीमत
- डेवलपर से इंडेक्सिंग के समय, एम्बेड किए गए डेटा के लिए शुल्क लिया जाता है. यह शुल्क, एम्बेड किए गए डेटा की मौजूदा कीमत के आधार पर लिया जाता है. फ़िलहाल, यह कीमत 10 लाख टोकन के लिए 15 रुपये है.
- स्टोरेज की सुविधा बिना किसी शुल्क के मिलती है.
- क्वेरी टाइम एम्बेडिंग की सुविधा बिना किसी शुल्क के उपलब्ध है.
- फ़ेच किए गए दस्तावेज़ टोकन के लिए, सामान्य कॉन्टेक्स्ट टोकन के तौर पर शुल्क लिया जाता है.
आगे क्या करना है
- फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाले स्टोर और फ़ाइल खोजने की सुविधा वाले दस्तावेज़ों के लिए, एपीआई रेफ़रंस देखें.
