Gemini can handle various types of input data, including text, images, and audio, at the same time.
This guide shows you how to work with media files using the Files API. The basic operations are the same for audio files, images, videos, documents, and other supported file types.
For file prompting guidance, check out the File prompt guide section.
Upload a file
You can use the Files API to upload a media file. Always use the Files API when the total request size (including the files, text prompt, system instructions, etc.) is larger than 100 MB. For PDF files, the limit is 50 MB.
The following code uploads a file and then uses the file in a call to
generateContent.
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file="path/to/sample.mp3")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview", contents=["Describe this audio clip", myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Describe this audio clip",
]),
});
console.log(response.text);
}
await main();
Go
file, err := client.Files.UploadFromPath(ctx, "path/to/sample.mp3", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer client.Files.Delete(ctx, file.Name)
resp, err := client.Models.GenerateContent(ctx, "gemini-3-flash-preview", []*genai.Content{
{
Parts: []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromFile(*file),
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
},
},
}, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
printResponse(resp)
REST
AUDIO_PATH="path/to/sample.mp3"
MIME_TYPE=$(file -b --mime-type "${AUDIO_PATH}")
NUM_BYTES=$(wc -c < "${AUDIO_PATH}")
DISPLAY_NAME=AUDIO
tmp_header_file=upload-header.tmp
# Initial resumable request defining metadata.
# The upload url is in the response headers dump them to a file.
curl "${BASE_URL}/upload/v1beta/files" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-D "${tmp_header_file}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Protocol: resumable" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: start" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Type: ${MIME_TYPE}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{'file': {'display_name': '${DISPLAY_NAME}'}}" 2> /dev/null
upload_url=$(grep -i "x-goog-upload-url: " "${tmp_header_file}" | cut -d" " -f2 | tr -d "\r")
rm "${tmp_header_file}"
# Upload the actual bytes.
curl "${upload_url}" \
-H "Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Offset: 0" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: upload, finalize" \
--data-binary "@${AUDIO_PATH}" 2> /dev/null > file_info.json
file_uri=$(jq ".file.uri" file_info.json)
echo file_uri=$file_uri
# Now generate content using that file
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{"text": "Describe this audio clip"},
{"file_data":{"mime_type": "${MIME_TYPE}", "file_uri": '$file_uri'}}]
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
Get metadata for a file
You can verify that the API successfully stored the uploaded file and get its
metadata by calling files.get.
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file='path/to/sample.mp3')
file_name = myfile.name
myfile = client.files.get(name=file_name)
print(myfile)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const fileName = myfile.name;
const fetchedFile = await ai.files.get({ name: fileName });
console.log(fetchedFile);
}
await main();
Go
file, err := client.Files.UploadFromPath(ctx, "path/to/sample.mp3", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
gotFile, err := client.Files.Get(ctx, file.Name)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println("Got file:", gotFile.Name)
REST
# file_info.json was created in the upload example
name=$(jq ".file.name" file_info.json)
# Get the file of interest to check state
curl https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/files/$name \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" > file_info.json
# Print some information about the file you got
name=$(jq ".file.name" file_info.json)
echo name=$name
file_uri=$(jq ".file.uri" file_info.json)
echo file_uri=$file_uri
List uploaded files
The following code gets a list of all the files uploaded:
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
print('My files:')
for f in client.files.list():
print(' ', f.name)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const listResponse = await ai.files.list({ config: { pageSize: 10 } });
for await (const file of listResponse) {
console.log(file.name);
}
}
await main();
Go
for file, err := range client.Files.All(ctx) {
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(file.Name)
}
REST
echo "My files: "
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/files" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY"
Delete uploaded files
Files are automatically deleted after 48 hours. You can also manually delete an uploaded file:
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file='path/to/sample.mp3')
client.files.delete(name=myfile.name)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const fileName = myfile.name;
await ai.files.delete({ name: fileName });
}
await main();
Go
file, err := client.Files.UploadFromPath(ctx, "path/to/sample.mp3", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
client.Files.Delete(ctx, file.Name)
REST
curl --request "DELETE" https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/files/$name \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY"
Usage info
You can use the Files API to upload and interact with media files. The Files API lets you store up to 20 GB of files per project, with a per-file maximum size of 2 GB. Files are stored for 48 hours. During that time, you can use the API to get metadata about the files, but you can't download the files. The Files API is available at no cost in all regions where the Gemini API is available.
File prompting strategies
This section provides guidance and best practices for using media files with prompts for the Gemini API.
Being able to use various types of data in your prompts gives you more flexibility in terms of what tasks you can tackle with the Gemini API. For example, you can send the model a photo of a delicious meal and ask it to write a short blog about the meal.
| Prompt | Response |
|
Write a short, engaging blog post based on this picture. It should include a description of the meal in the photo and talk about my journey meal prepping.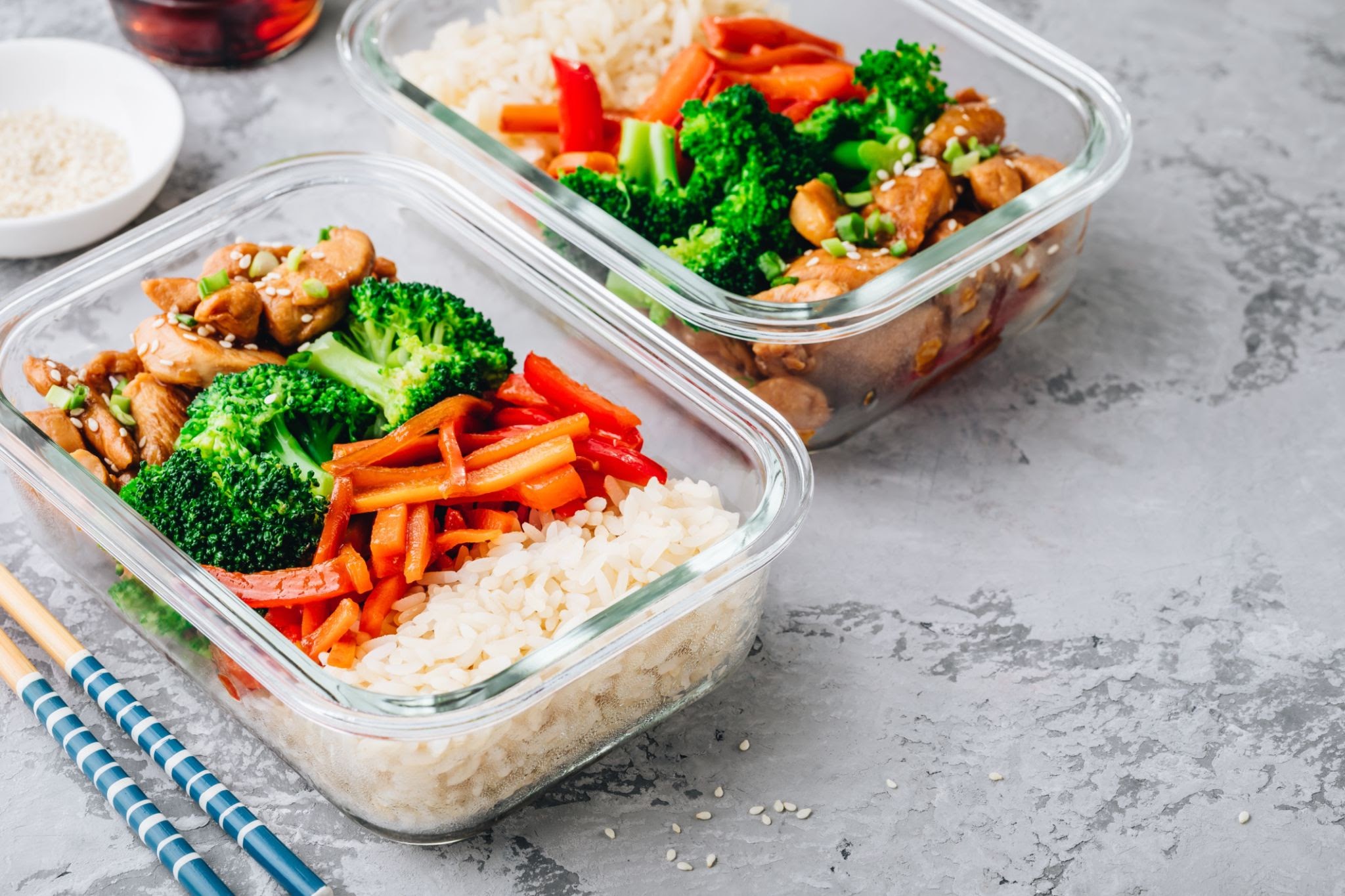 
|
Meal prepping is a great way to save time and money, and it can also help you to eat healthier. This meal is a great example of a healthy and delicious meal that can be easily prepped ahead of time. This meal features brown rice, roasted vegetables, and chicken teriyaki. The brown rice is a healthy and complex carbohydrate that will give you sustained energy. The roasted vegetables are a great way to get your daily dose of vitamins and minerals, and the chicken teriyaki is a delicious and protein-rich option. This meal is also very easy to prepare. Simply cook the brown rice, roast the vegetables, and cook the chicken teriyaki. Once everything is cooked, divide it into meal prep containers and store them in the refrigerator. You can then grab a container and go on busy mornings! If you're looking for a healthy and delicious meal that can be easily prepped ahead of time, this meal is a great option. It's packed with nutrients and flavor, and it's sure to keep you feeling full and satisfied. Here's to healthy and delicious meal prepping! |
If you are having trouble getting the output you want from prompts that use media files, there are some strategies that can help you get the results you want. The following sections provide design approaches and troubleshooting tips for improving prompts that use multimodal input.
You can improve your multimodal prompts by following these best practices:
-
Prompt design fundamentals
- Be specific in your instructions: Craft clear and concise instructions that leave minimal room for misinterpretation.
- Add a few examples to your prompt: Use realistic few-shot examples to illustrate what you want to achieve.
- Break it down step-by-step: Divide complex tasks into manageable sub-goals, guiding the model through the process.
- Specify the output format: In your prompt, ask for the output to be in the format you want, like markdown, JSON, HTML and more.
- Put your image first for single-image prompts: While Gemini can handle image and text inputs in any order, for prompts containing a single image, it might perform better if that image (or video) is placed before the text prompt. However, for prompts that require images to be highly interleaved with texts to make sense, use whatever order is most natural.
-
Troubleshooting your multimodal prompt
- If the model is not drawing information from the relevant part of the image: Drop hints with which aspects of the image you want the prompt to draw information from.
- If the model output is too generic (not tailored enough to the image/video input): At the start of the prompt, try asking the model to describe the image(s) or video before providing the task instruction, or try asking the model to refer to what's in the image.
- To troubleshoot which part failed: Ask the model to describe the image, or ask the model to explain its reasoning, to gauge the model's initial understanding.
- If your prompt results in hallucinated content: Try dialing down the temperature setting or asking the model for shorter descriptions so that it's less likely to extrapolate additional details.
- Tuning the sampling parameters: Experiment with different temperature settings and top-k selections to adjust the model's creativity.
Be specific in your instructions
Prompts have the most success when they are clear and detailed. If you have a specific output in mind, it's better to include that requirement in the prompt to ensure you get the output you want.
For this image of an airport board, asking the model to just "describe this image" could generate a general description. If you need the model to parse the time and city from the image, you can include that request directly in your prompt.
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|

Describe this image. |
The image shows an airport arrivals and departures board. |
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|
 Parse the time and city from the airport board shown in this image into a list. |
Add a few examples
The Gemini model can accept multiple inputs which it can use as examples to understand the output you want. Adding these examples can help the model identify the patterns and apply the relationship between the given images and responses to the new example. This is also called "few-shot" learning.
In the example below, the initial output is written in sentence form, and also contains the country (Brazil). Suppose you want the output in a different format or style, and you want only the city, not the country. Adding few-shot examples to your prompt can steer the model to respond in the way you want.
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|
 Determine the city along with the landmark. |
The landmark is the Christ the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. |
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|
|
Determine the city along with the landmark. 
|
city: Rome, landmark: the Colosseum. |

|
city: Beijing, landmark: Forbidden City |

|
city: Rio de Janeiro, landmark: Christ the Redeemer statue |
Break it down step-by-step
For complex tasks like the ones that require both visual understanding and reasoning, it can be helpful to split the task into smaller, more straightforward steps. Alternatively, it could also be effective if you directly ask the model to “think step by step” in your prompt.
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|
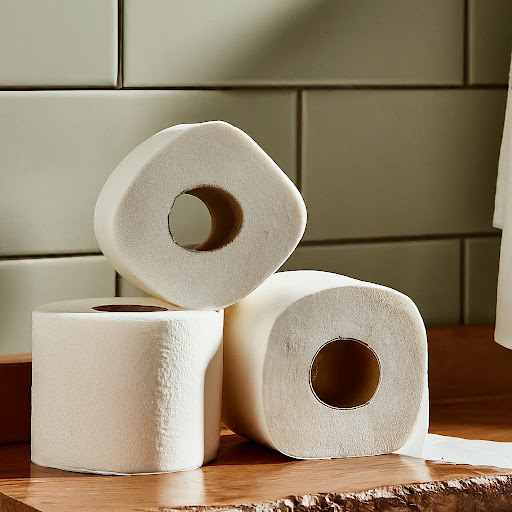

When will I run out of toilet paper? |
Soon, you only have 3 rolls left. |
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|

|
|
Math problems or other types of word problems are great candidates for asking the model to think step-by-step.
| Prompt | Response |
|---|---|
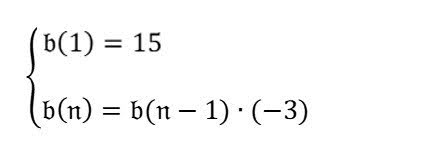
What is the 4th term in the sequence? |
-135 |
The response from the model is incorrect. Some ways to improve this is to ask the model to parse the problem before answering the prompt.
| Prompt | Response |
|---|---|
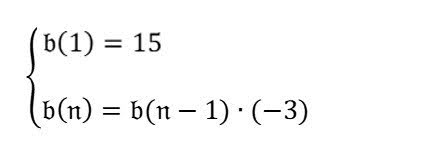
Parse the formula in the image first. Then based on the formula, answer "what's the 4th term in the sequence?". |
$$ b(n) = b(n-1) * (-3) $$ $$ b(1) = 15 $$ $$ b(4) = b(4-1) * (-3) $$ $$ b(4) = b(3) * (-3) $$ $$ b(3) = b(3-1) * (-3) $$ $$ b(3) = b(2) * (-3) $$ $$ b(2) = b(2-1) * (-3) $$ $$ b(2) = b(1) * (-3) $$ $$ b(2) = 15 * (-3) $$ $$ b(2) = -45 $$ $$ b(3) = b(2) * (-3) $$ $$ b(3) = -45 * (-3) $$ $$ b(3) = 135 $$ $$ b(4) = b(3) * (-3) $$ $$ b(4) = 135 * (-3) $$ $$ b(4) = -405 $$ Therefore, the 4th term in the sequence is -405. |
This model response is correct - now to make the response even more streamlined, you can ask the model to to think step-by-step.
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|
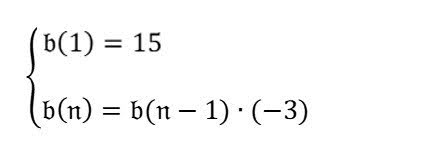
What is the 4th term in the sequence? Think step by step. |
The first term is 15. The second term is b(1) * (-3) = 15 * (-3) = -45. The third term is b(2) * (-3) = -45 * (-3) = 135. The fourth term is b(3) * (-3) = 135 * (-3) = -405. |
Specify the output format
A common problem is the need for model output to be in a certain format (e.g. markdown, JSON, HTML), especially if the model output needs to be ingested by a downstream task. You can try to produce output in that format by instructing the model to do so within the prompt. Below are two examples:
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|
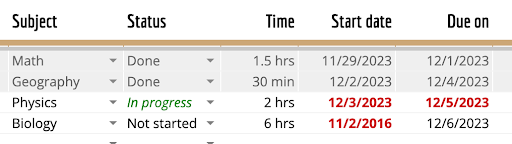
Parse the table in this image into markdown format |
| Subject | Status | Time | Start date | Due on | | ------- | ------ | ---- | ---------- | ------ | | Math | Done | 1.5 hrs | 11/29/2023 | 12/1/2023 | | Geography | Done | 30 min | 12/2/2023 | 12/4/2023 | | Physics | In progress | 2 hrs | 12/3/2023 | 12/5/2023 | | Biology | Not started | 6 hrs | 11/2/2016 | 12/6/2023 | |
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|
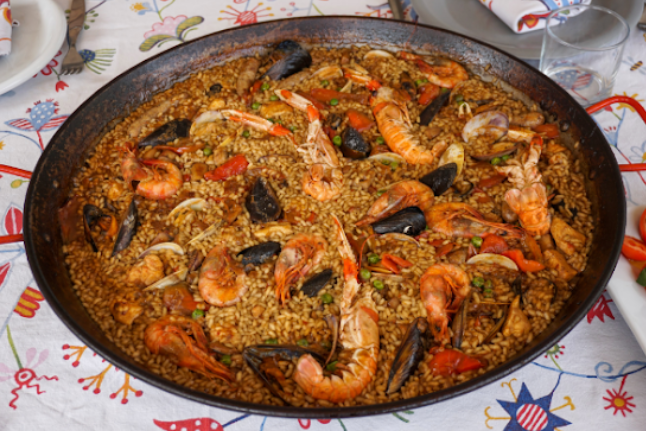

Provide a list of all the following attributes: ingredients, type of cuisine, vegetarian or not, in JSON format |
```json { "ingredients": [ "rice", "shrimp", "clams", "mussels", "peas", "tomatoes", "onions", "garlic", "olive oil", "paprika", "salt", "pepper" ], "type of cuisine": "Spanish", "vegetarian": false } ``` |
Put your image first for single-image prompts
While Gemini can interpret image and text in any order within a prompt, placing a single image before the text prompt might lead to better results. In the following samples, you'll notice the image comes first before the text in each prompt.
Troubleshooting your multimodal prompt
You might need to troubleshoot your prompt if you are not getting a helpful response. Here are a few strategies you could try.
If the model is not drawing information from the relevant part of the image
To get a more specific response, you can point out which aspects of the image you want the prompt to draw information from to inform its response.
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|

How many days will these diapers last a baby? |
The diapers will last for 198 days before they run out. |
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|

How long will these diapers last before I run out? Use the weight shown on the box to determine the child's age, and use the total number of diapers in the box. Divide the total number by how many diapers the child goes through per day. |
The box contains 198 diapers. The box states the diapers are for a child weighing 22-37 lbs. The average child in this weight range is likely between 1 and 2 years old. A 2-year-old typically goes through 6 diapers per day, therefore, the diapers will last around 33 days (198/6). |
If the model output is too generic and not tailored enough to the image input
To help the model tailor its response to the image(s), try asking it to describe the images before performing its reasoning task.
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|
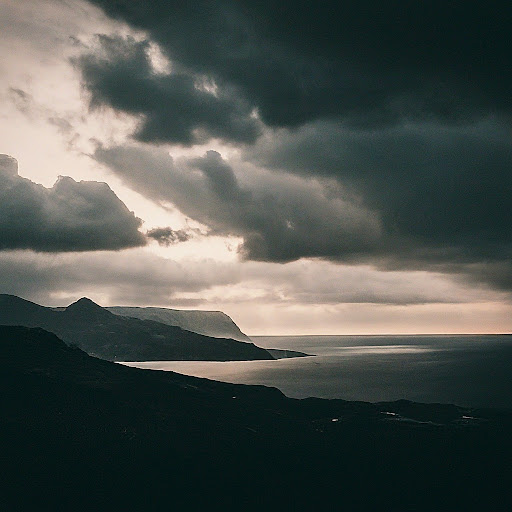




What is in common between these images? |
All four images are examples of landscape photography. |
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|




First, describe what's in each image in detail. What's in common between these images? |
The first image shows a person packing a suitcase. The second image shows an empty hallway in a shopping mall. The third image shows a roll of toilet paper. The fourth image shows a dark and stormy sea. The commonality between these images is that they are all examples of liminal spaces. Liminal spaces are places or situations that are in between two other places or situations. They are often characterized by a sense of uncertainty or ambiguity. The first image shows the person in between being at home and being on a trip. The second image shows the hallway in between two stores. The third image is of toilet paper, which can represent a bathroom. A bathroom is a transitional space between private and public realms. It's a place where we prepare ourselves to enter or leave the outside world. The fourth image shows the sea in between being calm and being stormy. Liminal spaces can be both exciting and unsettling. They can be a place of new beginning or a place of endings. They can be a place of reflection or a place of action. |
You can also try explicitly asking the model to refer to what's in the image.
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|




What is in common between these images? Refer to what's in the images in your response. |
All of the images are related to travel. The first image shows a person packing a suitcase, the second image shows an empty hallway in a shopping mall, the third image shows a stack of toilet paper, and the fourth image shows a dark and stormy sea. These images are all related to travel because they are all things that people need or use when they travel. The first image shows a person packing a suitcase, which is something that people do when they are going on a trip. The second image shows an empty hallway in a shopping mall, which is a place where people often go to buy things for their trips. The third image shows a stack of toilet paper, which is something that people often use when they are traveling. The fourth image shows a dark and stormy sea, which is something that people often encounter when they are traveling. |
The same tips work for creative output from images. In the following example with the rabbit, explicitly asking the model to include aspects from the image can improve the output.
| Prompt | Model response |
|---|---|
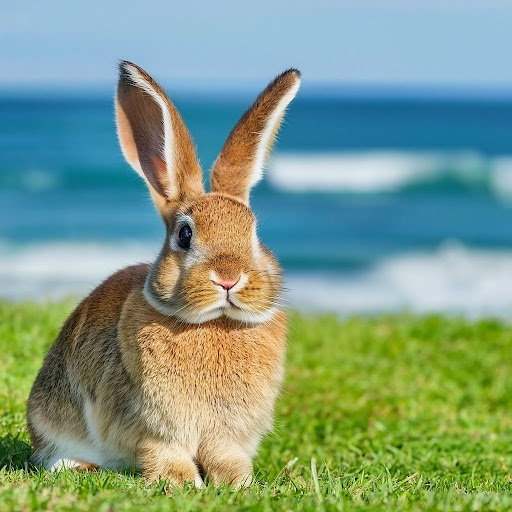

Can you write me a poem about this image? |
Little bunny, so soft and brown, You nibble on the grass, so green and sweet, |
| Updated prompt | Improved response |
|---|---|

Can you write me a descriptive and dramatic poem about this image and include the location? |
Little bunny on the green, Is it the ocean blue, Little bunny, tell me true, Perhaps it's the vastness of it all, Little bunny, I wonder what you dream, Whatever it may be, little bunny, |
Troubleshooting which part of the prompt failed
It can be hard to know whether a prompt failed because the model didn't understand the image to begin with, or if it did understand the image but did not perform the correct reasoning steps afterward. To disambiguate between those reasons, ask the model to describe what's in the image.
In the following example, if the model responds with a snack that seems surprising when paired with tea (e.g. popcorn), you can first troubleshoot to determine whether the model correctly recognized that the image contains tea.
| Prompt | Prompt for troubleshooting |
|---|---|

What's a snack I can make in 1 minute that would go well with this? |

Describe what's in this image. |
Another strategy is to ask the model to explain its reasoning. That can help you narrow down which part of the reasoning broke down, if any.
| Prompt | Prompt for troubleshooting |
|---|---|

What's a snack I can make in 1 minute that would go well with this? |

What's a snack I can make in 1 minute that would go well with this? Please explain why. |
What's next
- Try writing your own multimodal prompts using Google AI Studio.
- For information on using the Gemini Files API for uploading media files and including them in your prompts, see the Vision, Audio, and Document processing guides.
- For more guidance on prompt design, like tuning sampling parameters, see the Prompt strategies page.
