Gemini API 提供代码执行工具,可让模型生成和运行 Python 代码。然后,模型可以根据代码执行结果进行迭代学习,直到获得最终输出。您可以利用代码执行功能来构建可受益于基于代码的推理的应用。例如,您可以使用代码执行功能来求解方程式或处理文本。您还可以使用代码执行环境中包含的库来执行更专业的任务。
Gemini 只能执行 Python 代码。您仍然可以要求 Gemini 以其他语言生成代码,但模型无法使用代码执行工具来运行该代码。
启用代码执行功能
如需启用代码执行功能,请在模型上配置代码执行工具。这样一来,模型便可生成并运行代码。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
const parts = response?.candidates?.[0]?.content?.parts || [];
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode && part.executableCode.code) {
console.log(part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult && part.codeExecutionResult.output) {
console.log(part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
});
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
genai.Text("What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."),
config,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d ' {"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": {
"parts":
{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}
},
}'
输出可能如下所示,为了便于阅读,已对其进行格式设置:
Okay, I need to calculate the sum of the first 50 prime numbers. Here's how I'll
approach this:
1. **Generate Prime Numbers:** I'll use an iterative method to find prime
numbers. I'll start with 2 and check if each subsequent number is divisible
by any number between 2 and its square root. If not, it's a prime.
2. **Store Primes:** I'll store the prime numbers in a list until I have 50 of
them.
3. **Calculate the Sum:** Finally, I'll sum the prime numbers in the list.
Here's the Python code to do this:
def is_prime(n):
"""Efficiently checks if a number is prime."""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n <= 3:
return True
if n % 2 == 0 or n % 3 == 0:
return False
i = 5
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0 or n % (i + 2) == 0:
return False
i += 6
return True
primes = []
num = 2
while len(primes) < 50:
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
num += 1
sum_of_primes = sum(primes)
print(f'{primes=}')
print(f'{sum_of_primes=}')
primes=[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67,
71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151,
157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229]
sum_of_primes=5117
The sum of the first 50 prime numbers is 5117.
此输出结合了模型在使用代码执行功能时返回的多个内容部分:
text:模型生成的内嵌文本executableCode:由模型生成且旨在执行的代码codeExecutionResult:可执行代码的结果
这些部分的命名惯例因编程语言而异。
使用图片执行代码 (Gemini 3)
Gemini 3 Flash 模型现在可以编写和执行 Python 代码,主动操纵和检查图片。
用例
- 缩放和检查:模型会隐式检测细节何时过小(例如,读取远处的仪表),并编写代码来裁剪和重新检查更高分辨率的区域。
- 视觉数学:模型可以使用代码运行多步计算(例如,对收据上的各个项目求和)。
- 图片注释:模型可以注释图片以回答问题,例如绘制箭头来显示关系。
启用图片代码执行功能
Gemini 3 Flash 正式支持使用图片执行代码。您可以同时启用“将代码执行作为工具”和“思考”来激活此行为。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
from PIL import Image
import io
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
image = types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes, mime_type="image/jpeg"
)
# Ensure you have your API key set
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[image, "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
if part.as_image() is not None:
# display() is a standard function in Jupyter/Colab notebooks
display(Image.open(io.BytesIO(part.as_image().image_bytes)))
JavaScript
async function main() {
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({ });
// 1. Prepare Image Data
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
// 2. Call the API with Code Execution enabled
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
{
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
},
{ text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?" }
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
// 3. Process the response (Text, Code, and Execution Results)
const candidates = result.candidates;
if (candidates && candidates[0].content.parts) {
for (const part of candidates[0].content.parts) {
if (part.text) {
console.log("Text:", part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(`\nGenerated Code (${part.executableCode.language}):\n`, part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(`\nExecution Output (${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}):\n`, part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
}
}
}
main();
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initialize Client (Reads GEMINI_API_KEY from env)
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 1. Download the image
imageResp, err := http.Get("https://goo.gle/instrument-img")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer imageResp.Body.Close()
imageBytes, err := io.ReadAll(imageResp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 2. Configure Code Execution Tool
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
// 3. Generate Content
result, err := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
[]*genai.Content{
{
Parts: []*genai.Part{
{InlineData: &genai.Blob{MIMEType: "image/jpeg", Data: imageBytes}},
{Text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"},
},
Role: "user",
},
},
config,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 4. Parse Response (Text, Code, Output)
for _, cand := range result.Candidates {
for _, part := range cand.Content.Parts {
if part.Text != "" {
fmt.Println("Text:", part.Text)
}
if part.ExecutableCode != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nGenerated Code (%s):\n%s\n",
part.ExecutableCode.Language,
part.ExecutableCode.Code)
}
if part.CodeExecutionResult != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nExecution Output (%s):\n%s\n",
part.CodeExecutionResult.Outcome,
part.CodeExecutionResult.Output)
}
}
}
}
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MODEL="gemini-3-flash-preview"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/$MODEL:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{
"inline_data": {
"mime_type":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
},
{"text": "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"}
]
}],
"tools": [
{
"code_execution": {}
}
]
}'
在对话中使用代码执行
您还可以在对话中使用代码执行功能。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
chat = client.chats.create(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
response = chat.send_message("I have a math question for you.")
print(response.text)
response = chat.send_message(
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import {GoogleGenAI} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
history: [
{
role: "user",
parts: [{ text: "I have a math question for you:" }],
},
{
role: "model",
parts: [{ text: "Great! I'm ready for your math question. Please ask away." }],
},
],
config: {
tools: [{codeExecution:{}}],
}
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({
message: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
});
console.log("Chat response:", response.text);
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
chat, _ := client.Chats.Create(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
config,
nil,
)
result, _ := chat.SendMessage(
ctx,
genai.Part{Text: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and " +
"make sure you get all 50.",
},
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "Can you print \"Hello world!\"?"
}]
},{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": ""
},
{
"executable_code": {
"language": "PYTHON",
"code": "\nprint(\"hello world!\")\n"
}
},
{
"code_execution_result": {
"outcome": "OUTCOME_OK",
"output": "hello world!\n"
}
},
{
"text": "I have printed \"hello world!\" using the provided python code block. \n"
}
],
},{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}]
}
]
}'
输入/输出 (I/O)
从 Gemini 2.0 Flash 开始,代码执行支持文件输入和图表输出。利用这些输入和输出功能,您可以上传 CSV 和文本文件,询问有关这些文件的问题,并让系统在回答中为您生成 Matplotlib 图表。输出文件以内嵌图片的形式在响应中返回。
I/O 定价
使用代码执行 I/O 时,您需要为输入 token 和输出 token 支付费用:
输入 token:
- 用户提示
输出 token 数:
- 由模型生成的代码
- 代码环境中的代码执行输出
- 思考令牌
- 模型生成的摘要
I/O 详情
使用代码执行 I/O 时,请注意以下技术细节:
- 代码环境的最长运行时间为 30 秒。
- 如果代码环境生成错误,模型可能会决定重新生成代码输出。此过程最多可重复 5 次。
- 文件输入大小上限受模型 token 窗口的限制。在 AI Studio 中,使用 Gemini Flash 2.0 时,输入文件大小上限为 100 万个 token(对于支持的输入类型的文本文件,大约为 2MB)。如果您上传的文件过大,AI Studio 将不允许您发送该文件。
- 代码执行最适合处理文本文件和 CSV 文件。
- 输入文件可以采用
part.inlineData或part.fileData格式(通过 Files API 上传),输出文件始终以part.inlineData格式返回。
结算
通过 Gemini API 启用代码执行功能不会产生额外的费用。系统会根据您使用的 Gemini 模型,按当前的输入和输出 token 费率向您收费。
以下是关于代码执行结算的一些其他事项:
- 您只需为传递给模型的输入 token 支付一次费用,并需要为模型返回给您的最终输出 token 支付费用。
- 表示生成的代码的 token 会计为输出 token。生成的代码可以包含文本和多模态输出结果(例如图片)。
- 代码执行结果也会计为输出 token。
结算模式如下图所示:
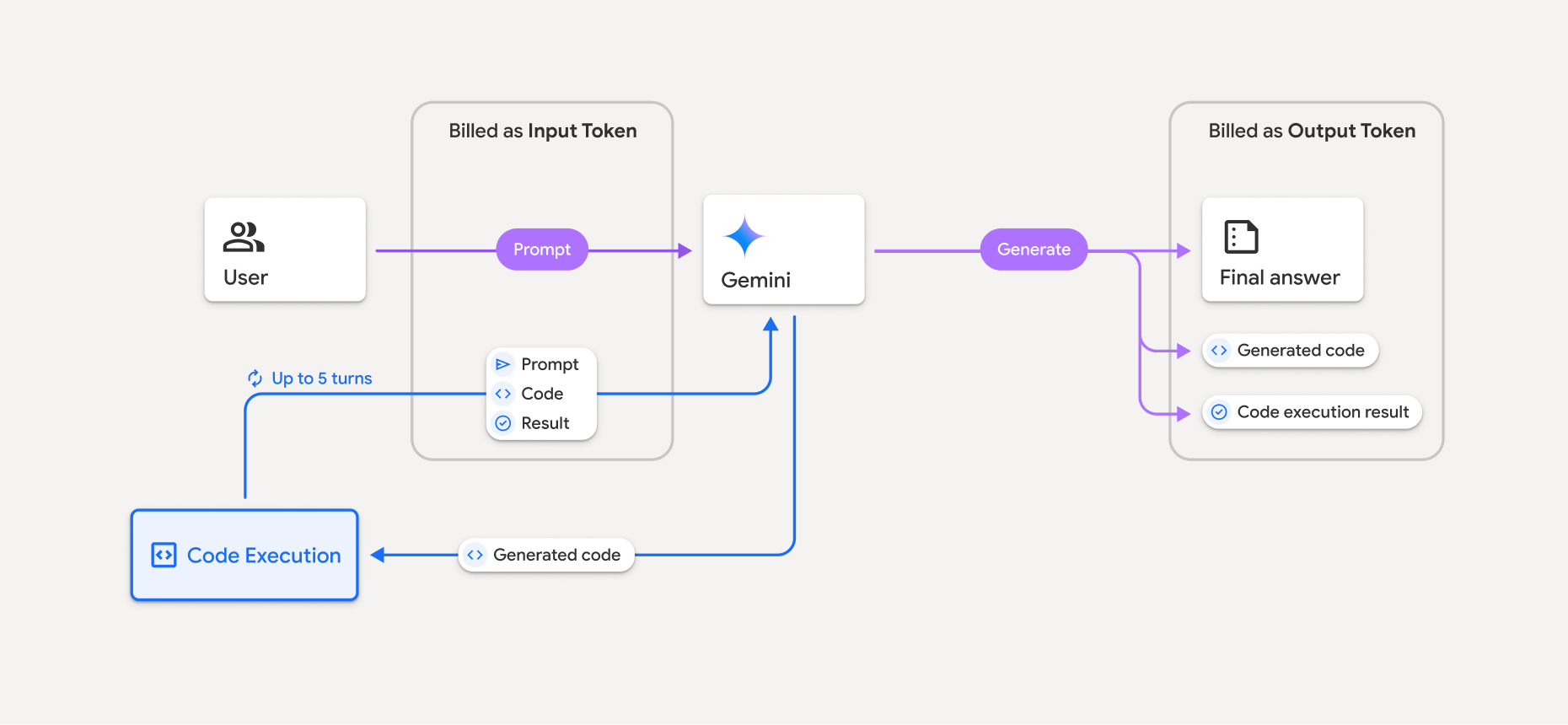
- 系统会根据您使用的 Gemini 模型,按当前的输入和输出 token 费率向您收费。
- 如果 Gemini 在生成回答时使用了代码执行功能,则原始提示、生成的代码以及已执行代码的相应结果会被标记为中间 token,并会按输入 token 计费。
- 然后,Gemini 会生成摘要,并返回生成的代码、已执行代码的相应结果以及最终摘要。这些内容会按输出 token 计费。
- Gemini API 在 API 响应中包含中间 token 数,因此您可以了解为什么会获得除初始提示之外的其他输入 token。
限制
- 该模型只能生成和执行代码。它无法返回其他制品,例如媒体文件。
- 在某些情况下,启用代码执行功能可能会导致模型输出的其他方面(例如,编写故事)出现回归问题。
- 不同模型成功使用代码执行功能的能力各不相同。
支持的工具组合
代码执行工具可以与依托 Google 搜索进行接地功能结合使用,以处理更复杂的用例。
受支持的库
代码执行环境包含以下库:
- attrs
- 国际象棋
- contourpy
- fpdf
- geopandas
- imageio
- jinja2
- joblib
- jsonschema
- jsonschema-specifications
- lxml
- matplotlib
- mpmath
- numpy
- opencv-python
- openpyxl
- 打包
- pandas
- pillow
- protobuf
- pylatex
- pyparsing
- PyPDF2
- python-dateutil
- python-docx
- python-pptx
- reportlab
- scikit-learn
- scipy
- seaborn
- six
- striprtf
- sympy
- tabulate
- TensorFlow
- toolz
- xlrd
您无法安装自己的库。
后续步骤
- 试用代码执行 Colab。
- 了解其他 Gemini API 工具:
