Google 検索によるグラウンディングは、Gemini モデルをリアルタイムのウェブ コンテンツに接続し、 利用可能なすべての言語で動作します。これにより、 Gemini はより正確な回答を提供し、知識の カットオフを超えて検証可能なソースを引用できます。
グラウンディングは、次のようなアプリの構築に役立ちます。
- 事実の正確性を高める: 実世界の情報を基に 回答することで、モデルのハルシネーションを減らします。
- リアルタイムの情報にアクセスする: 最近のイベントや トピックに関する質問に回答します。
引用を提供する: モデルの主張のソースを示すことで、ユーザーの信頼を築きます。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
grounding_tool = types.Tool(
google_search=types.GoogleSearch()
)
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[grounding_tool]
)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Who won the euro 2024?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const groundingTool = {
googleSearch: {},
};
const config = {
tools: [groundingTool],
};
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Who won the euro 2024?",
config,
});
console.log(response.text);
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{"text": "Who won the euro 2024?"}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"google_search": {}
}
]
}'
詳しくは、検索ツール ノートブックをお試しください。
Google 検索によるグラウンディングの仕組み
google_search ツールを有効にすると、モデルは情報の検索、処理、引用のワークフロー全体
を自動的に処理します。
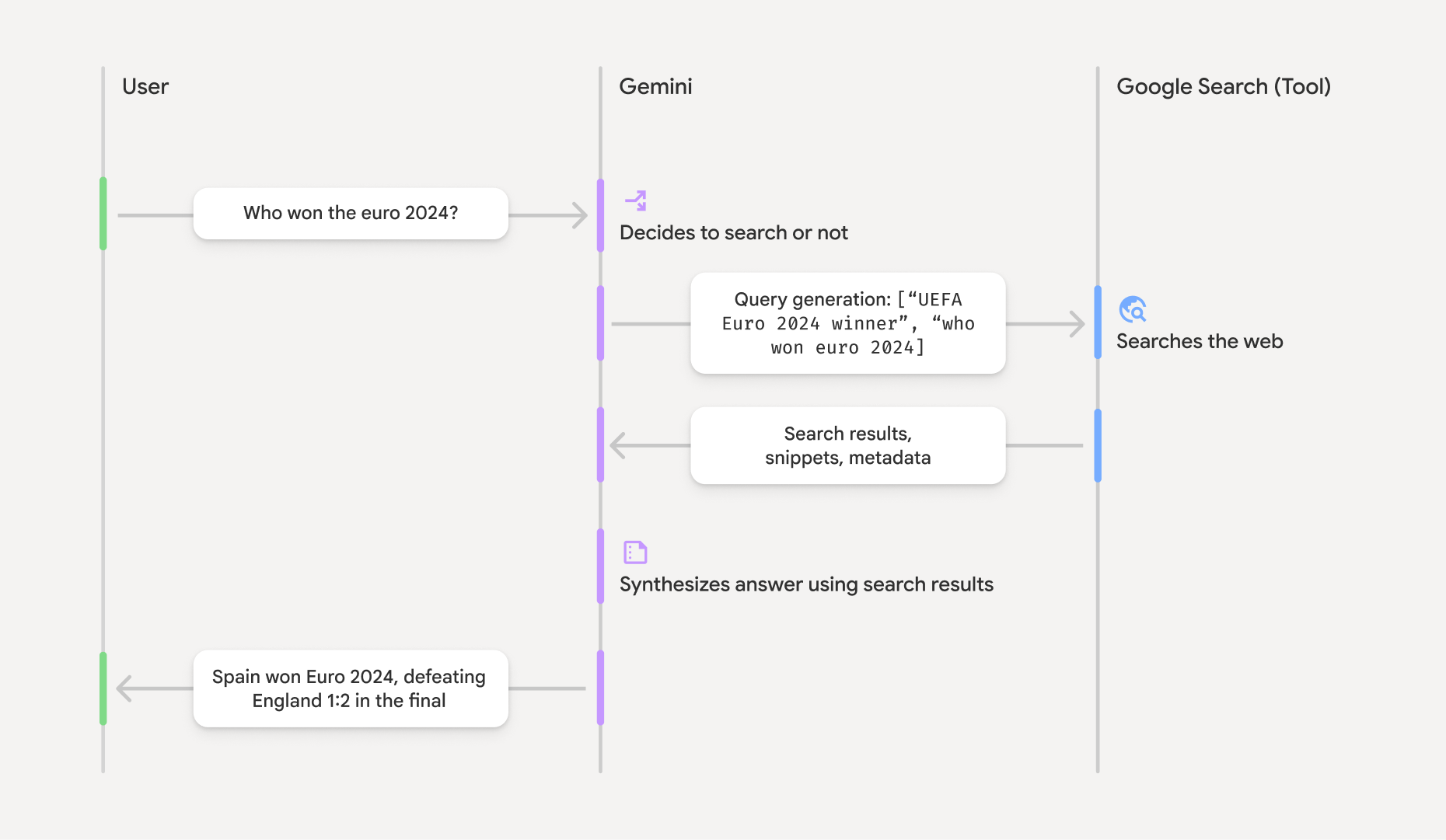
- ユーザー プロンプト: アプリケーションは、ユーザーのプロンプトを Gemini API に送信します
。
google_searchツールが有効になっています。 - プロンプトの分析: モデルはプロンプトを分析し、 Google 検索で回答を改善できるかどうかを判断します。
- Google 検索: 必要に応じて、モデルは 1 つ以上の 検索クエリを自動的に生成して実行します。
- 検索結果の処理: モデルは検索結果を処理し、 情報を合成してレスポンスを作成します。
- グラウンディングされたレスポンス: API は、検索結果に基づいてグラウンディングされた、最終的なユーザー フレンドリーなレスポンスを返します。このレスポンスには、モデルのテキスト
回答と、
groundingMetadata検索クエリ、ウェブ検索結果、引用を含む が含まれます。
グラウンディング レスポンスについて
レスポンスが正常にグラウンディングされると、レスポンスに
groundingMetadata フィールドが含まれます。この構造化データは、
主張を検証し、アプリで豊富な引用エクスペリエンスを構築するために不可欠です。
{
"candidates": [
{
"content": {
"parts": [
{
"text": "Spain won Euro 2024, defeating England 2-1 in the final. This victory marks Spain's record fourth European Championship title."
}
],
"role": "model"
},
"groundingMetadata": {
"webSearchQueries": [
"UEFA Euro 2024 winner",
"who won euro 2024"
],
"searchEntryPoint": {
"renderedContent": "<!-- HTML and CSS for the search widget -->"
},
"groundingChunks": [
{"web": {"uri": "https://vertexaisearch.cloud.google.com.....", "title": "aljazeera.com"}},
{"web": {"uri": "https://vertexaisearch.cloud.google.com.....", "title": "uefa.com"}}
],
"groundingSupports": [
{
"segment": {"startIndex": 0, "endIndex": 85, "text": "Spain won Euro 2024, defeatin..."},
"groundingChunkIndices": [0]
},
{
"segment": {"startIndex": 86, "endIndex": 210, "text": "This victory marks Spain's..."},
"groundingChunkIndices": [0, 1]
}
]
}
}
]
}
Gemini API は、groundingMetadata とともに次の情報を返します。
webSearchQueries: 使用された検索クエリの配列。これは、 デバッグやモデルの推論プロセスの把握に役立ちます。searchEntryPoint: 必要な検索 候補をレンダリングするための HTML と CSS が含まれています。完全な使用要件については、利用規約をご覧ください。groundingChunks: ウェブソース(uriとtitle)を含むオブジェクトの配列。groundingSupports: モデルのレスポンスtextをgroundingChunksのソースに接続するチャンクの配列。各チャンクは、テキストsegment(startIndexとendIndexで定義)を 1 つ以上のgroundingChunkIndicesにリンクします。これは、インライン引用を作成するための鍵となります。
Google 検索によるグラウンディングは、URL コンテキスト ツールと組み合わせて使用して、パブリック ウェブデータと指定した特定の URL の両方でレスポンスをグラウンディングすることもできます。
インライン引用でソースを帰属させる
API は構造化された引用データを返すため、ユーザー インターフェースでのソースの表示方法を完全に制御できます。groundingSupports
と groundingChunks フィールドを使用して、モデルのステートメントをソースに直接リンクできます。メタデータを処理して、インラインのクリック可能な引用を含む
レスポンスを作成する一般的なパターンを次に示します。
Python
def add_citations(response):
text = response.text
supports = response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata.grounding_supports
chunks = response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata.grounding_chunks
# Sort supports by end_index in descending order to avoid shifting issues when inserting.
sorted_supports = sorted(supports, key=lambda s: s.segment.end_index, reverse=True)
for support in sorted_supports:
end_index = support.segment.end_index
if support.grounding_chunk_indices:
# Create citation string like [1](link1)[2](link2)
citation_links = []
for i in support.grounding_chunk_indices:
if i < len(chunks):
uri = chunks[i].web.uri
citation_links.append(f"[{i + 1}]({uri})")
citation_string = ", ".join(citation_links)
text = text[:end_index] + citation_string + text[end_index:]
return text
# Assuming response with grounding metadata
text_with_citations = add_citations(response)
print(text_with_citations)
JavaScript
function addCitations(response) {
let text = response.text;
const supports = response.candidates[0]?.groundingMetadata?.groundingSupports;
const chunks = response.candidates[0]?.groundingMetadata?.groundingChunks;
// Sort supports by end_index in descending order to avoid shifting issues when inserting.
const sortedSupports = [...supports].sort(
(a, b) => (b.segment?.endIndex ?? 0) - (a.segment?.endIndex ?? 0),
);
for (const support of sortedSupports) {
const endIndex = support.segment?.endIndex;
if (endIndex === undefined || !support.groundingChunkIndices?.length) {
continue;
}
const citationLinks = support.groundingChunkIndices
.map(i => {
const uri = chunks[i]?.web?.uri;
if (uri) {
return `[${i + 1}](${uri})`;
}
return null;
})
.filter(Boolean);
if (citationLinks.length > 0) {
const citationString = citationLinks.join(", ");
text = text.slice(0, endIndex) + citationString + text.slice(endIndex);
}
}
return text;
}
const textWithCitations = addCitations(response);
console.log(textWithCitations);
インライン引用を含む新しいレスポンスは次のようになります。
Spain won Euro 2024, defeating England 2-1 in the final.[1](https:/...), [2](https:/...), [4](https:/...), [5](https:/...) This victory marks Spain's record-breaking fourth European Championship title.[5]((https:/...), [2](https:/...), [3](https:/...), [4](https:/...)
料金
Gemini 3 で Google 検索によるグラウンディングを使用する場合、プロジェクトにはモデルが実行すると判断した検索クエリごとに課金されます。モデルが 1 つのプロンプトに回答するために複数の検索クエリを実行すると判断した場合(たとえば、同じ API 呼び出し内で "UEFA Euro 2024 winner" と "Spain vs England Euro 2024 final
score" を検索する場合)、そのリクエストに対してツールの有料使用が 2 回カウントされます。課金目的では、一意のクエリをカウントする際に空のウェブ検索クエリは無視されます
。この課金モデルは Gemini 3
モデルにのみ適用されます。Gemini 2.5 以前のモデルで検索グラウンディングを使用する場合、お客様の
プロジェクトにはプロンプトごとに課金されます。
料金の詳細については、Gemini API の料金 ページをご覧ください。
サポートされているモデル
完全な機能については、モデル 概要ページをご覧ください。
| モデル | Google 検索によるグラウンディング |
|---|---|
| Gemini 3.1 Flash Image プレビュー | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3.1 Pro プレビュー | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Pro Image プレビュー | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash プレビュー | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ |
サポートされているツールの組み合わせ
Google 検索によるグラウンディングは、コード実行や URL コンテキストなどの他のツールと組み合わせて使用して、より複雑なユースケースを実現できます。
