This guide provides instructions for converting Gemma models in Hugging Face
Safetensors format (.safetensors) into the MediaPipe Task file format
(.task). This conversion is essential for deploying either pre-trained or
fine-tuned Gemma models for on-device inference on Android and iOS using the
MediaPipe LLM Inference API and LiteRT runtime.
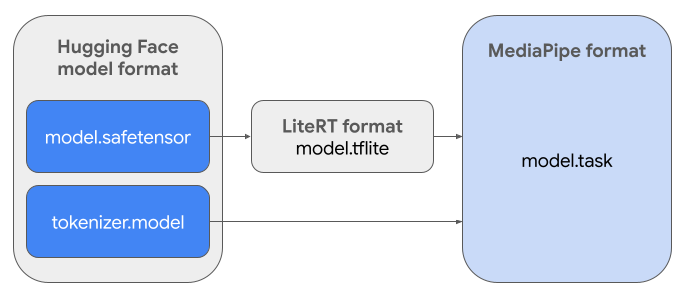
To create the required Task Bundle (.task), you will use
LiteRT Torch. This tool exports PyTorch models into
multi-signature LiteRT (.tflite) models, which are compatible with the
MediaPipe LLM Inference API and suitable for running on CPU backends in mobile
applications.
The final .task file is a self-contained package required by MediaPipe,
bundling the LiteRT model, the tokenizer model, and essential metadata. This
bundle is necessary because the tokenizer (which converts text prompts into
token embeddings for the model) must be packaged with the LiteRT model to
enable end-to-end inference.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
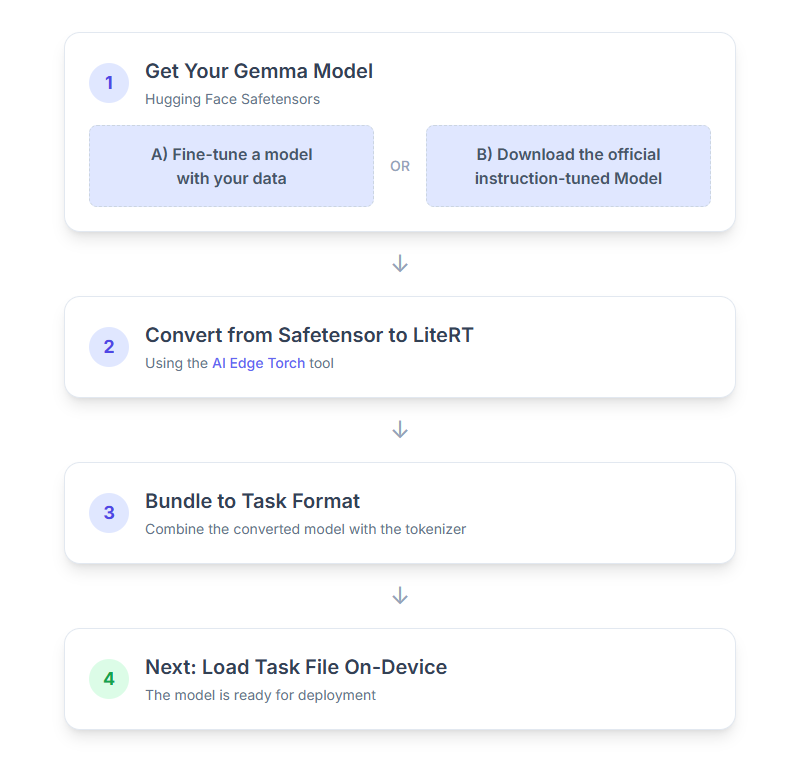
1. Get Your Gemma model
You have two options to get started.
Option A. Use an Existing Fine-Tuned Model
If you have a fine-tuned Gemma model prepared, just proceed to the next step.
Option B. Download the official instruction-tuned Model
If you need a model, you can download an instruction-tuned Gemma from the Hugging Face Hub.
Setup necessary tools:
python -m venv hfsource hf/bin/activatepip install huggingface_hub[cli]
Download the model:
Models on the Hugging Face Hub are identified by a model ID, typically in the
format <organization_or_username>/<model_name>. For example, to download the
official Google Gemma 3 270M instruction-tuned model, use:
hf download google/gemma-3-270m-it --local-dir "PATH_TO_HF_MODEL"#"google/gemma-3-1b-it", etc
2. Convert and quantize the model to LiteRT
Set up a Python virtual environment and install the latest stable release of the LiteRT Torch package:
python -m venv litert-torchsource litert-torch/bin/activatepip install "litert-torch>=0.8.0"
Use the following script to convert the Safetensor into LiteRT model.
from litert_torch.generative.examples.gemma3 import gemma3
from litert_torch.generative.utilities import converter
from litert_torch.generative.utilities.export_config import ExportConfig
from litert_torch.generative.layers import kv_cache
pytorch_model = gemma3.build_model_270m("PATH_TO_HF_MODEL")
# If you are using Gemma 3 1B
#pytorch_model = gemma3.build_model_1b("PATH_TO_HF_MODEL")
export_config = ExportConfig()
export_config.kvcache_layout = kv_cache.KV_LAYOUT_TRANSPOSED
export_config.mask_as_input = True
converter.convert_to_tflite(
pytorch_model,
output_path="OUTPUT_DIR_PATH",
output_name_prefix="my-gemma3",
prefill_seq_len=2048,
kv_cache_max_len=4096,
quantize="dynamic_int8",
export_config=export_config,
)
Be aware that this process is time-consuming and depends on your computer's processing speed. For reference, on a 2025 8-core CPU, a 270M model takes over 5-10 minutes, while a 1B model can take approximately 10-30 minutes.
The final output, a LiteRT model, will be saved to your specified
OUTPUT_DIR_PATH.
Tune the following values based on the memory and performance constraints of your target device.
kv_cache_max_len: Defines the total allocated size of the model's working memory (the KV cache). This capacity is a hard limit and must be sufficient to store the combined sum of the prompt's tokens (the prefill) and all subsequently generated tokens (the decode).prefill_seq_len: Specifies the token count of the input prompt for prefill chunking. When processing the input prompt using prefill chunking, the entire sequence (e.g., 50,000 tokens) is not computed at once; instead, it's broken into manageable segments (e.g., chunks of 2,048 tokens) that are loaded sequentially into the cache to prevent an out-of-memory error.quantize: string for the selected quantization schemes. Following is the list of available quantization recipes for Gemma 3.none: No quantizationfp16: FP16 weights, FP32 activations and floating point computation for all opsdynamic_int8: FP32 activations, INT8 weights, and integer computationweight_only_int8: FP32 activations, INT8 weights, and floating point computation
3. Create a Task Bundle from LiteRT and tokenizer
Set up a Python virtual environment and install mediapipe Python package:
python -m venv mediapipesource mediapipe/bin/activatepip install mediapipe
Use the genai.bundler library to bundle the model:
from mediapipe.tasks.python.genai import bundler
config = bundler.BundleConfig(
tflite_model="PATH_TO_LITERT_MODEL.tflite",
tokenizer_model="PATH_TO_HF_MODEL/tokenizer.model",
start_token="<bos>",
stop_tokens=["<eos>", "<end_of_turn>"],
output_filename="PATH_TO_TASK_BUNDLE.task",
prompt_prefix="<start_of_turn>user\n",
prompt_suffix="<end_of_turn>\n<start_of_turn>model\n",
)
bundler.create_bundle(config)
The bundler.create_bundle function creates a .task file that contains all
the necessary information to run the model.
4. Inference with Mediapipe on Android
Initialize the task with basic configuration options:
// Default values for LLM models
private object LLMConstants {
const val MODEL_PATH = "PATH_TO_TASK_BUNDLE_ON_YOUR_DEVICE.task"
const val DEFAULT_MAX_TOKEN = 4096
const val DEFAULT_TOPK = 64
const val DEFAULT_TOPP = 0.95f
const val DEFAULT_TEMPERATURE = 1.0f
}
// Set the configuration options for the LLM Inference task
val taskOptions = LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath(LLMConstants.MODEL_PATH)
.setMaxTokens(LLMConstants.DEFAULT_MAX_TOKEN)
.build()
// Create an instance of the LLM Inference task
llmInference = LlmInference.createFromOptions(context, taskOptions)
llmInferenceSession =
LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llmInference,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTopK(LLMConstants.DEFAULT_TOPK)
.setTopP(LLMConstants.DEFAULT_TOPP)
.setTemperature(LLMConstants.DEFAULT_TEMPERATURE)
.build(),
)
Use the generateResponse() method to generate a text response.
val result = llmInferenceSession.generateResponse(inputPrompt)
logger.atInfo().log("result: $result")
To stream the response, use the generateResponseAsync() method.
llmInferenceSession.generateResponseAsync(inputPrompt) { partialResult, done ->
logger.atInfo().log("partial result: $partialResult")
}
See the LLM Inference guide for Android for more information.
Next steps
Build and explore more with Gemma models:
